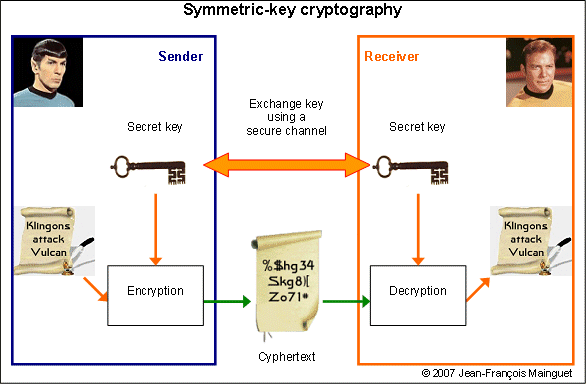
https://fingerchip.pagesperso-orange.fr/biometrics/cryptography.htm
AES, Advanced Encryption System, is a symmetric key algorithm, used worldwide to encrypt confidential information. A symmetric key algorithm, also known as secret key cryptography, is an encryption algorithm that uses the same key for encryption and decryption. The algorithm used in the encoding and decoding process can be announced over an unsecured channel. The code will remain uncracked as long as the key used remains secret. These encryption algorithms have no publicly known computationally feasible inverse algorithms or attack capable of recovering the original message without the decryption key. Instead all known attacks involve brute force to break. The issue with secret key cryptography is how do the users exchange a secret key without the potential for eavesdroppers to find out the secret key and therefore the encrypted information.
One solution to the dilema of sharing the secret key securely is using public key cryptography. One party can send out a public key to allow anyone to send an encrypted message to them. However, they have a correlated secret key which allows only the party with the secret key to decode the message. This will allow both parties to get the secret key securely.
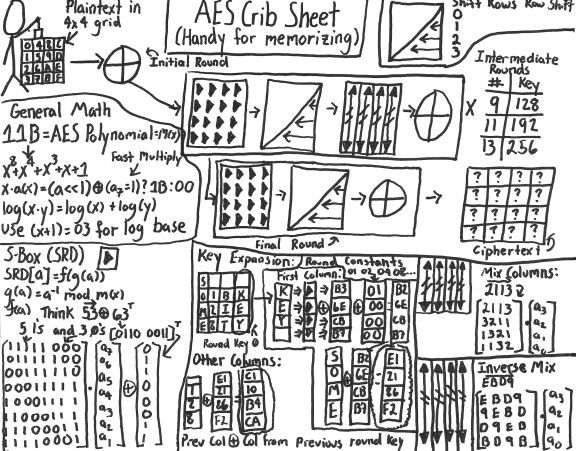
https://www.moserware.com/2009/09/stick-figure-guide-to-advanced.html
How AES Works:
1. Share a secret key.
2. Load the message/data into a 4x4 matrix. The matrix is known as a state matrix.
3. Next XOR each byte in the matrix with the byte in the first round key (the secret key). XOR is used as XOR is fast and inexpensive, as minimal hardware is needed and no 'carrying' bits are required as the calculation can be done in parallel.
4. Additonal keys are created from the original key using a remixing technique. The last column (4) from the previous key is used. The bottom bit is moved from the bottom to the top. Each byte is ran through a substitution box to map the value to another value. The result is then XOR with a round contant, which varies each round. Lastly, the result is XOR with the first problem of the previous round key. Lastly the result is XOR with the same column in the previous round key.
5. Now a encrypted message had been produced.
6. To decrypt, the reverse process is done, starting with the final key, the encrypted message, working the way back to the message using the secret key.
