What is a Qubit?
A qubit is a quantum bit, made out of particles such as photons, electrons or ions. Most frequently, a qubit is a photon. A qubit is based upon the foundation of a particle’s quantum nature, particularly the quantum property of superposition. A bit, whether classical or quantum, is the simplest unit of information.
In a qubit, all single quantum states correspond to a point on or inside the qubit. Every axis corresponds to a single quantum measurement, and every measurement changes the state of the qubit to match the result of the measurement. Rotating the qubit around an axis can change the state of the qubit. Rotation is the one method to change the state of a qubit without introducing randomness or collapsing the system.
A qubit was discovered with the double slit experiment. All a qubit is is a particle observed in a quantum nature. The start of qubits started with the start of quantum mechanics. Click here to learn about the double slit experiment.
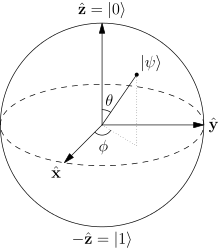
Bloch Sphere representation of a qubit. The probability amplitudes in the text are given by  and
and 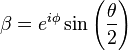 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Qubit
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Qubit
